| Administrator Handbook | Table of contents |
|
This documentation page of the LoriotPro Software concerns the WEB interface of the product.
In addition to its graphical interface in Windows™, the LoriotPro software integrates an HTTP server and thus offers a multi-user GUI in a WEB interface. The data collected by the software in SNMP or by other means are accessible via this interface. Numerous charts, histograms, tables, assist you and give you information of states and of performance on the infrastructure monitored.
Terminology reminder: Hosts are devices of all types having an IP address and must be declared in the directory of LoriotPro.
The IP routing table of the host displays for each local or remote IP network the IP address of reference to which the host must send its packets.
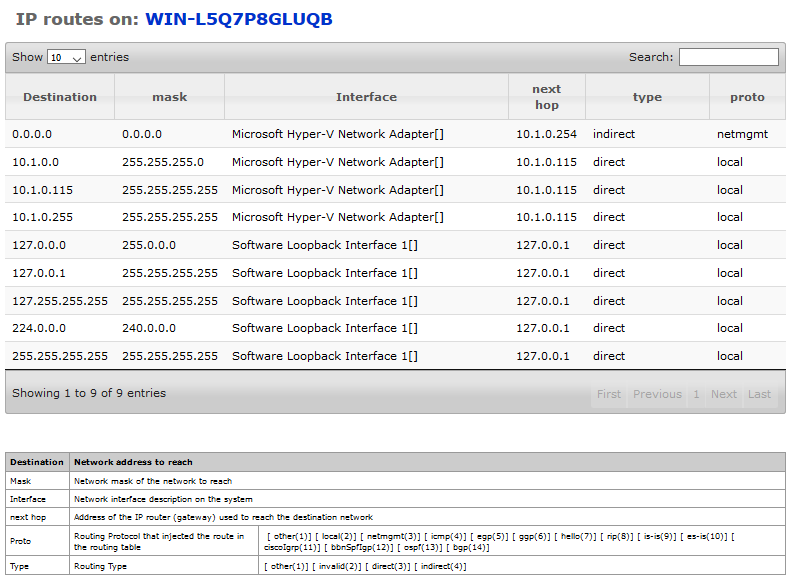
Destination |
The destination IP address of this route. Ed an entry with a value of 0.0.0.0 is considered as the default route. Multiple routes to a single destination may appear in the table, but access to these multiple entries depends on the table access mechanisms defined by the current network management protocol. |
Mask |
Specifies the logical-AND mask with the destination address before being compared with the value of the years ipRouteDest field. For systems that do not support arbitrary subnet masks, an agent builds the value of the ipRouteMask by determining whether the value of the ipRouteDest field belongs to a class-A, B, or C network, and then using l Any of the following: Network of masks If the value of the ipRouteDest is 0.0.0.0 (the default route), the mask value is also 0.0.0.0. It should be noted that all IP routings and subsystems implicitly use this mechanism. |
Interface |
Index and description of the interface |
Next hop |
IP address of next hop on this route. (In the case of a li ed route to an interface that is realized via e a broadcast media, the value of this field is the IP address of the interface agent.) |
Type |
The type of itin éraire. Note that the Direct (3) and indirect (4) values refer to the notion of direct and indirect IP architecture routing. Put this item on the value invalid (2) invalid entry in the ipRouteTable object. |
Protocol |
The routing m echanism by which this route has been entered in the table. Inclusion of values by a routing protocol does not mean that the host supports it. Routing protocols: other (1)] [local (2)] [netmgmt (3)] [icmp (4)] [egp (5)] [ggp (6)] [hello (7)] [rip ( (11)] [bbnSpfIgp (12)] [ospf (13)] [bgp (14)] [is-is (9) |
 www.loriotpro.com
www.loriotpro.com |
|